November 21, 2024
- Our Services
- Platforms
- Target Solutions
- Technologies
- Service Types
- Our Science
- About Us
- Contact us
November 21, 2024
Phosphorylation is a common type of post translational modifications (PTM), with more than 30% of proteins in cells phosphorylated. It is one of the most fundamental, prevalent, and important mechanisms to regulate and control protein activity and function, and is involved in various physiological and pathological processes, regulating cellular activities such as proliferation, development, differentiation, and apoptosis.
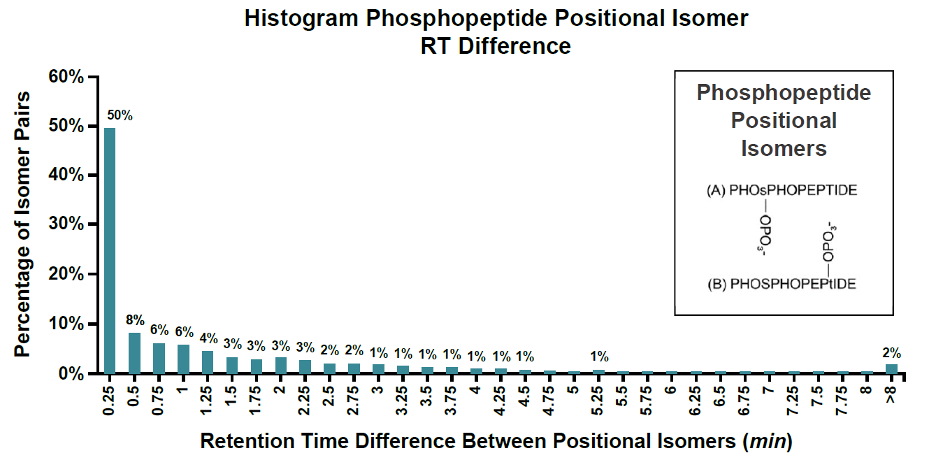
Phosphorylation on different sites on the same peptide can lead to phosphopeptide isomers co-elution on chromatography. These co-eluted phosphopeptide isomers cannot be separated on conventional LC-MS/MS platforms. According to available statistics, at least 26% of phosphopeptides have isomers, 50% of which cannot be effectively differentiated on chromatography, making it difficult to identify phosphorylation sites.
Immobilized metal affinity chromatography (IMAC) strategy: using proprietary targeted antibodies to enrich phosphopeptides, to reduce sample complexity
Additional ion mobility separation enables more reliable and deeper coverage for phosphorylation
Strict dual quality control to remove low confident data: false discovery rate (FDR, 1%); false localization rate (FLR, 0.75)
Upgraded bioinformatic analysis available: kinase prediction, signaling analysis, and data mining
4D technology brings a dramatic increase in detection depth and sensitivity.
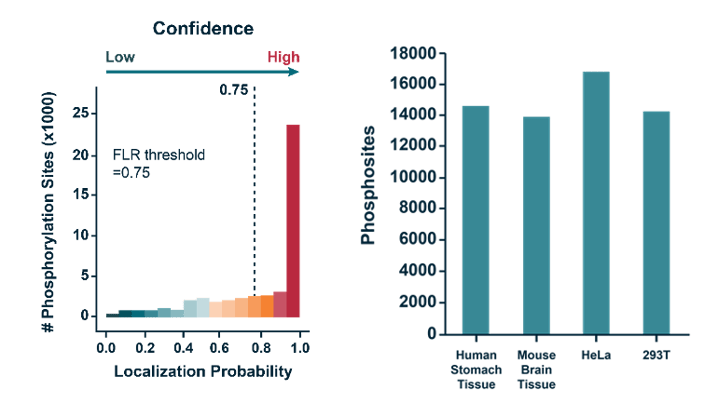
>10,000 phosphorylation sites (localization probability > 0.75) were identified with high confidence in various cell tissues, 50% higher than the traditional method.
4D phosphoproteomics resolves the issue of isomerization in PTM through ion mobility separation, which ensures more reliable identification of PTMs.
As shown in the figure, the elution time and mass-to-charge ratio of many phosphorylated peptide isomers are identical, but the structural differences of the phosphorylation locations can be effectively detected by ion mobility. 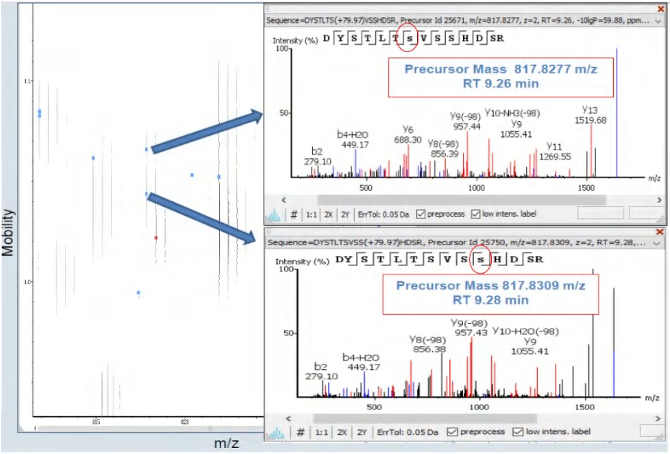
The separation of both ion mobility and HPLC can maximize the identification and differentiation of these co-eluted modified peptide signals.
Publication
Mouse Stromal Cells Confound Proteomic Characterization and Quantification of Xenograft Models
Poster
Systematic Evaluation of Label-Free Protein Quantification Pipelines (DDA vs DIA)
© 2024 Crown Bioscience. All Rights Reserved.


© 2024 Crown Bioscience. All Rights Reserved. Privacy Policy
2023-12-28
2022-12-08
site_page
Proteomics