What is DMPK and what is ADME?
DMPK (Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics) and ADME (Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and Excretion) are closely related concepts in pharmacology and drug development, but they differ in scope and focus. DMPK refers to the study of how a drug is metabolized (broken down) and how it moves through the body (pharmacokinetics).
ADME (Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and Excretion) describes the four core processes a drug undergoes in the body:
- Absorption: How a drug enters the bloodstream (e.g., through the gut or skin).
- Distribution: How the drug spreads to tissues and organs.
- Metabolism: How the drug is chemically altered, primarily in the liver.
- Excretion: How the drug and its metabolites are eliminated from the body (e.g., urine, feces).
How do DMPK and ADME differ?
DMPK involves designing experiments and models to predict and optimize a drug's pharmacokinetics and metabolism. It helps determine dosing, drug formulation, and safety profiles.
ADME forms the foundation of understanding drug behavior but doesn't typically include the broader kinetic modeling or systemic interactions studied in DMPK. DMPK and ADME studies are performed throughout the drug development process. In vitro studies are often used to screen a large number of compounds, while in vivo studies are often performed later in development. In vivo studies can help identify areas of concern, such as low absorption or high clearance.
Why are DMPK/ADME studies important?
DMPK/ADME studies are critical in drug development as they provide insights into how a drug behaves in the body. These studies ensure that the drug reaches its intended target at the right concentration, has minimal side effects, and is effectively cleared from the system. By understanding these properties, researchers can optimize drug efficacy, safety, and dosing regimens, reducing the risk of late-stage failures in clinical trials.
Why choose Crown Bioscience DMPKT service?
We provide a one-stop and innovative DMPKT service for small molecule, therapeutic antibody, ADC as well as novel drug modalities from early discovery to IND submission during drug development.
As a comprehensive DMPK service provider, we established extensive capabilities which are including:
- In vitro ADME/In vivo PK/Bioanalytical science/ADC and new modalities DMPK/Toxicity
- Competitive throughput, TAT and price for service offering
By leveraging our current core platforms/expertise (PDX, PDO, in vitro, biomarker), we offer integrated solutions for pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamic to support preclinical pharmacology research.
What PK/PD capability can Crown Bioscience offer?
- Dose-response relationship: The effects of a substance at varying doses is analyzed against the desired pharmacological response, evaluating the optimal dose range, in turn determining if the drug achieves the required therapeutic outcome.
- Effective dosage range: PK/PD studies will aid in identifying the therapeutic range of the drug or substance, contributing to the optimization of dosing regiments, and lowering the risk of adverse effects.
- Identifying Biomarkers: Specific biomarkers will be identified, indicating the efficacy and safety of the substance, these biomarkers can be used to monitor responses during clinical trials, streamline the development of drugs, and personalize treatment approaches.
- Interactions between substances: The pharmacodynamic interactions between the target drug and other substances can be assessed, allowing the development of drug combination strategies, along with predicting potential adverse effects, and optimizing therapeutic regimens.
- Predictive modelling: Development of predictive models that will simulate the drug’s effect in different scenarios, helping forecast drug responses, optimizing dosing strategies, and informing decisions throughout the development process and clinical trial design.
Does Crown offer ADC DMPK and Tox service? If yes, what assays will be conducted for ADC PK in early discovery and preclinical stage?
Yes. Crown provides integrated solution for ADC DMPK and Tox evaluation. Below are general assays for ADC PK/PD and safety assessment based on guideline and white papers.
- In vitro stability: Plasma/Serum/Whole blood, Lysosome, Liver S9/ liver homogenate, 2D/3D cell line
- Bioanalysis and DAR characterization: intact and subunit of ADC, DAR stability and distribution link to efficacy and safety, payload release metabolites (if necessary)
- Full animal PK: rodent and non-rodent PK
- PK/PD: PK/PD and MOA in CDX/PDX model, Biodistribution
- Tox: exploratory toxicity and TK
Does Crown provide exploratory tox service for different therapeutics?
Yes. Crown has general animal tox capability along with strong biomarker and bioanalysis investigations. Potential specialties services to include in vitro, organoid and HuGEMM platforms.
Can you provide DMPK service for new drug IND submission?
Yes. We provide PK service for IND enabling. This includes:
- Drug PK screening (Hit-to-Lead, Lead Optimization)
- Regular animal PK (single dose or repeat dose)
- Comprehensive Efficacy and PK/PD in pharmacological models
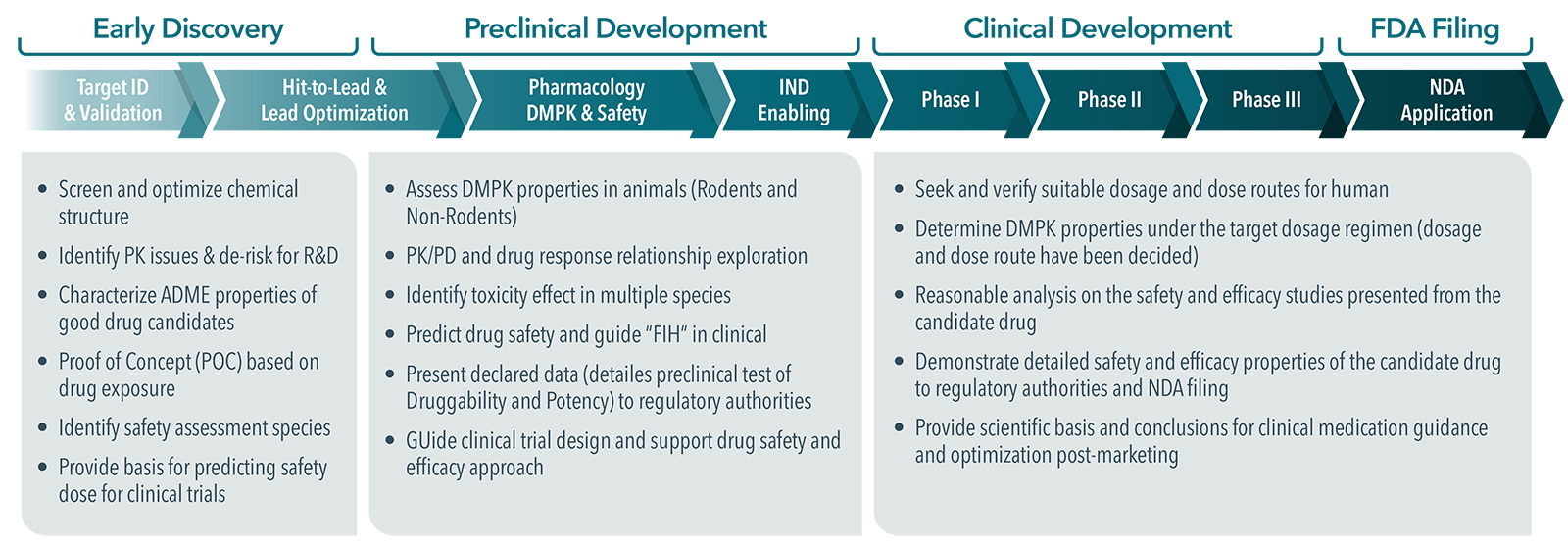
At what stage in drug discovery do you conduct DMPK/ADME study?
DMPK/ADME studies are conducted throughout the drug discovery and development process, with specific focus and objectives at different stages:
- Early Discovery (Lead Optimization): Initial ADME screening is performed to assess the drug-like properties of lead compounds. This includes solubility, permeability, metabolic stability, and potential drug-drug interactions to select the best candidates for further development.
- Preclinical Development: More detailed DMPK studies are conducted in vitro and in vivo to evaluate pharmacokinetics (PK), bioavailability, and toxicity. These studies help refine dosing strategies and predict human outcomes.
- Clinical Development: During clinical trials, DMPK studies continue to assess PK and metabolism in humans, validate dose adjustments, and monitor drug-drug interactions.
By conducting DMPK/ADME studies at each stage, researchers can identify potential issues early, optimize lead compounds, and improve the likelihood of clinical success.
What are the key assays used in ADME/DMPK studies?
Common assays include solubility testing, permeability studies (e.g., Caco-2), metabolic stability and enzyme inhibition assays, plasma protein binding studies, bioavailability assessments, and pharmacokinetic profiling.
How do ADME properties affect drug efficacy and safety?
Good ADME properties ensure a drug reaches its target site at the right concentration without accumulating to toxic levels or causing adverse effects. Poor ADME properties can result in low efficacy, high toxicity, or unpredictable behavior in the body.
How are in vitro and in vivo ADME studies different?
In vitro studies use controlled environments like cell cultures or enzymes to predict a drug’s behavior, while in vivo studies involve animal or human models to observe the actual effects in a living system.
What role does DMPK play in pharmacokinetics?
DMPK provides a framework for understanding the absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion of drugs, which directly impacts pharmacokinetics. This helps determine optimal dosing and frequency to achieve desired therapeutic outcomes.
How can poor ADME properties lead to drug failure?
Poor ADME properties can lead to inadequate bioavailability, rapid clearance, toxic accumulation, or failure to reach the target site. These issues often result in inefficacy or unacceptable side effects, causing drug candidates to fail in preclinical or clinical stages.